Explanation
In this code, a persistent segment tree is built for each node in the tree by creating a new version based on its parent’s segment tree.
First, a persistent segment tree for the root node, which shows the frequency of the values encountered, is built. We set all of the values of this tree to zeros. To incorporate the value of the current node, we create a new version of the segment tree by adding nodes to the parent’s tree and incrementing the segment tree node corresponding to the current node’s value. We store the root node of the new version of the tree for future reference. This way, we don't need to build a completely new tree and modify only the necessary nodes while reusing the unchanged parts.
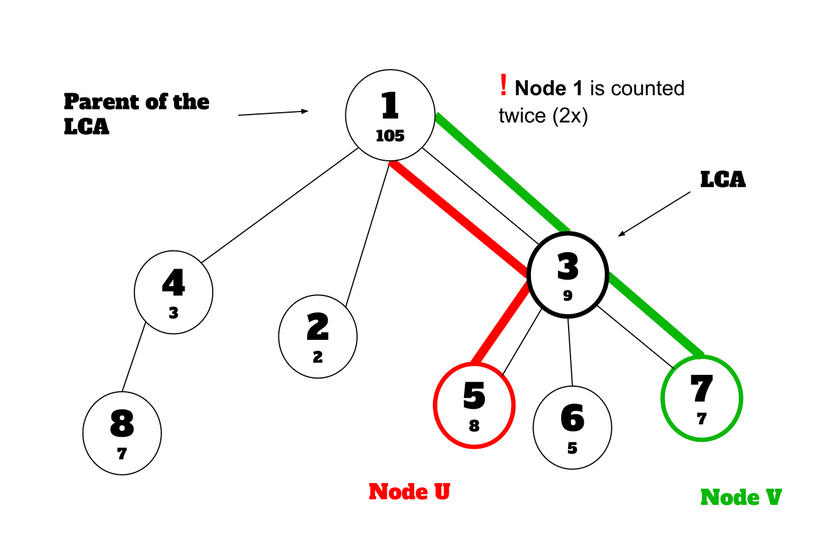
Each persistent segment tree keeps the frequency of numbers on the way from the root of the tree given in the input to itself. When asked for the kth minimum node in the path of to , the code first determines the lowest common ancestor (LCA) of the tree in the input using binary lifting. Next, we run a binary search using the frequency values from the persistent segment tree versions of four nodes: , , the LCA, and the parent of the LCA.
Since the values that are not on the path of and , but on the path from the root node to the nodes and are also counted in their persistent segment trees, just considering their persistent segment trees would produce the wrong results.
Handling Overcounting
We subtract the frequencies of nodes from the root node to the LCA and its parent because we count the nodes twice from the root node to the LCA. In addition, since the LCA is on the path of to , we subtract the frequencies from the LCA and the parent of the LCA to consider the value of the LCA.
This formula tracks the frequencies of values in the left subtree of the persistent segment tree along the path from to .
Value compression is used to effectively handle large numbers.
Implementation
Time Complexity:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;int timer = 0;const int MAX_NODES_GRAPH = 1e5;struct PersistentSegmentTree {static const int MAX_NODES_TREE = 2e6;int left_child[MAX_NODES_TREE + 1];int right_child[MAX_NODES_TREE + 1];int frequency[MAX_NODES_TREE + 1];
Join the USACO Forum!
Stuck on a problem, or don't understand a module? Join the USACO Forum and get help from other competitive programmers!